ADC converts the relationship between range and accuracy
An ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) converts an analog signal into a digital signal by discretizing the input signal. The relationship between the range and accuracy of an ADC is a crucial factor in determining its performance.
The range of an ADC refers to the minimum and maximum values that can be measured by the converter. For example, a 12-bit ADC with a range of 0 to 5 volts can measure 2^12 (4096) different values within that range.
The accuracy of an ADC refers to the degree of error in the conversion process. It is the difference between the measured value and the true value of the input signal. Accuracy is typically expressed as a percentage of the full-scale range. For example, a 12-bit ADC with an accuracy of ±1% can measure the input voltage within ±1% of the full-scale range, or within ±0.05 volts in the case of a 5-volt range.
The relationship between range and accuracy in an ADC is that increasing the range typically decreases the accuracy of the conversion. This is because the same number of bits is used to represent a larger range of values, resulting in a lower resolution and increased quantization error.
For example, a 12-bit ADC with a 5-volt range and ±1% accuracy can measure a voltage with a resolution of 5/4096 volts per bit or approximately 1.22 mV. If the range is increased to 10 volts, the resolution decreases to 2.44 mV per bit, resulting in decreased accuracy.
Therefore, when selecting an ADC, it is important to consider the tradeoff between range and accuracy and choose the appropriate combination for the intended application.
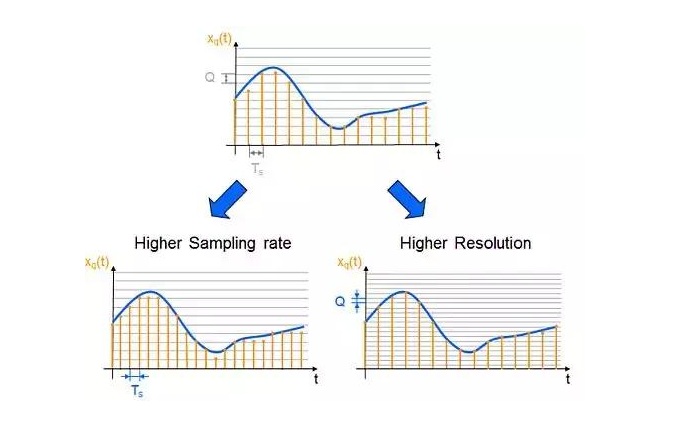
ADC转换量程和精度的关系
ADC(模数转换器)通过离散化输入信号将模拟信号转换为数字信号。 ADC 的范围和精度之间的关系是决定其性能的关键因素。
ADC 的范围是指转换器可以测量的最小值和最大值。例如,范围为 0 至 5 伏的 12 位 ADC 可以测量该范围内的 2^12 (4096) 个不同值。
ADC的精度是指转换过程中的误差程度。它是测量值与输入信号的真实值之间的差异。精度通常表示为满量程范围的百分比。例如,精度为 ±1% 的 12 位 ADC 可以测量满量程范围的 ±1% 以内的输入电压,或者在 5 伏范围的情况下测量 ±0.05 伏以内的输入电压。
ADC 中范围和精度之间的关系是,增加范围通常会降低转换精度。这是因为使用相同数量的比特来表示更大范围的值,导致较低的分辨率和增加的量化误差。
例如,具有 5 伏范围和 ±1% 精度的 12 位 ADC 可以测量分辨率为每位 5/4096 伏或大约 1.22 mV 的电压。如果范围增加到 10 伏,分辨率将降低到每位 2.44 mV,从而导致精度降低。
因此,在选择 ADC 时,重要的是要权衡范围和精度,并为预期应用选择合适的组合。